TOP PAGE > Information on Disaster Risk Reduction of the Member Countries
Information on Disaster Risk Reduction of the Member Countries
 Thailand
Thailand
General Information
 Formal Name: Kingdom of Thailand
Formal Name: Kingdom of ThailandThailand is located in the center of Indochina and northern part of Malay Peninsula. It is bordered by Cambodia to the east, Laos to the north, Myanmar and the Andaman Sea to the west, and the Gulf of Thailand and Malaysia to the south, covering the area of 514,000 square kilometres. Thailand has mountainous area in northern part, and Menam Chao Phraya delta in the central part which is one of the greatest rice-growing areas in the world. The climate is a tropical climate which has rainy season from May to October. In the north and central regions, it has high precipitation from August to October, which causes frequent floods.
The capital is Bangkok. Total population stood at 66.09 millions.
Overview of Disasters
Flood, landslide, forest fire, wind damage, drought, lightening, hail and epidemics are the major disasters.
Recent Major Disasters
Indian Ocean Tsunami (December 2004)
On 26 December 2004, Tsunami occurred off the Sumatra Island killed 5,395, affected 58,550, and whose total loss was US$ 399.78 million in Thailand.
Flood (Jul. 2011-Jan. 2012)
Severe flooding occurred during the 2011 monsoon season in Thailand, beginning at the end of July and ceasing mid-January 2012. The flooding affected the provinces of Northern, Northeastern and Central Thailand along the Mekong and Chao Phraya river basins, as well as parts of the capital city of Bangkok. It resulted in a total of 813 deaths, 9.5 million people affected and economic damage of USD40 billion.
Typhoon Noru (September 2022)
Typhoon Noru was an intense tropical cyclone that affected Vietnam, Thailand and Philippines. The heavy rain caused severe flooding and landslides across parts of Thailand. Department of Disaster Prevention and Mitigation (DDPM) reported that 37 districts in 18 provinces in North Northeast and Central region have been hit by flooding between 22-26 September 2022. Around 4,000 people were evacuated, 4.348 households were affected and 3 people were deaths.
The heavy rain has continued since then, causing further flooding and rivers to rise. The authorities issued warnings for communities close to the Chao Phraya river and Pa Sak river on 2nd October. Until 5th October the rivers were above critical level in 38 locations, mostly in Northern and central provinces. DDPM reported floods and flash floods occurred in 25 provinces with approximately 156,240 households affected 4 deaths and 2 injuries.
The heavy rain has continued since then, causing further flooding and rivers to rise. The authorities issued warnings for communities close to the Chao Phraya river and Pa Sak river on 2nd October. Until 5th October the rivers were above critical level in 38 locations, mostly in Northern and central provinces. DDPM reported floods and flash floods occurred in 25 provinces with approximately 156,240 households affected 4 deaths and 2 injuries.
Disaster Management System
Legal System
The Disaster Prevention and Mitigation Act 2007 (DPM Act) has replaced the old and outdated 1979 Civil Defence Act and the 1999 Fire Prevention and Suppression Act. It entered into force on 6 November 2007. It stipulates the Department of Disaster Prevention and Mitigation (DDPM) as the core government department in handling national disaster management work. Also it authorizes local governments to take responsibility of disaster management in their respective areas, in line with the Provincial Plan.
This Act has served as the principal legal mechanism for disaster risk management practices in Thailand, coupled with an application of other disaster risk management related laws/regulations/notifications/directives.
This Act has served as the principal legal mechanism for disaster risk management practices in Thailand, coupled with an application of other disaster risk management related laws/regulations/notifications/directives.
Organization
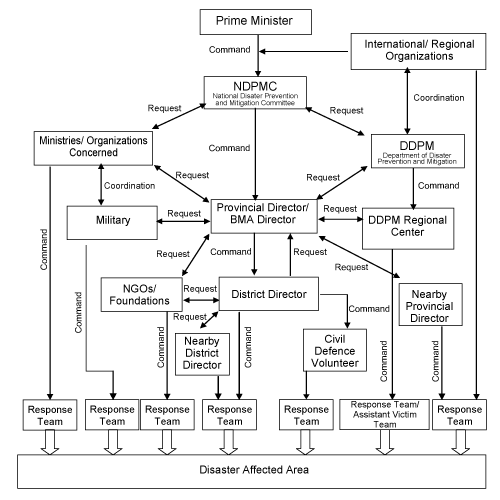 At national level, the National Disaster Prevention and Mitigation Committee (NDPMC) chaired by the Prime Minister or designated Deputy Prime Minister has prominent tasks and responsibilities for policy-making on disaster risk management. At local level, the Provincial Disaster Prevention and Mitigation Committee and Bangkok Metropolitan Committee are formed.
At national level, the National Disaster Prevention and Mitigation Committee (NDPMC) chaired by the Prime Minister or designated Deputy Prime Minister has prominent tasks and responsibilities for policy-making on disaster risk management. At local level, the Provincial Disaster Prevention and Mitigation Committee and Bangkok Metropolitan Committee are formed.Department of Disaster Prevention and Mitigation (DDPM) was established under Ministry of Interior as the prime agency for coordinating disaster risk management activities by all related organizations at all levels.
Disaster Prevention and Mitigation Academy (DPMA) was established for human resource development for disaster reduction.
Plan
The National Disaster Risk Management Plan 2021-2027 has the purpose to be a a concept of operation in handing national disaster management actions for all relevant agencies. The Plan will serve as a tool for reducing the impact of disaster, realizing disaster risk management standards in every community as well as for further integrating disaster risk reduction thinking and methods into the national sustainable development process. In addition, the Plan is a master plan for provinces and districts to develop the Provincial/District Disaster Risk Management Plans, as well as Provincial/District Multi-hazard Specific Action Plans on Disaster Risk Management for the purpose of directing, coordinating, and providing support for disaster management efforts of the local administrative organization. The plan is regularly revised and will be presented as a new plan for cabinet approval before launch.
ADRC Counterpart
Country Report
Country Report 2023 (English Version, PDF file)Country Report 2022 (English Version, PDF file)
Country Report 2021 (English Version, PDF file)
Country Report 2020 (English Version, PDF file)
Country Report 2019 (English Version, PDF file)
Country Report 2018 (English Version, PDF file)
Country Report 2017 (English Version, PDF file)
Country Report 2016 (English Version, PDF file)
Country Report 2012 (English Version, PDF file)
Country Report 2011 (English Version, PDF file)
Country Report 2010 (English Version, PDF file)
Country Report 2009 (English Version, PDF file)
Country Report 2008 (English Version, PDF file)
Country Report 2006 (Japanese Version, PDF file)
Country Report 2006 (English Version, PDF file)
Country Report 2004 (English Version, PDF file)
Country Report 2003 (English Version, PDF file)
Country Report 1999 (English Version, PDF file)
Country Report 1999 (Japanese Version, PDF file)
Country Report 1998 (English Version, PDF file)

