3 Accumulation and Provision of Information on Natural Disasters and Disaster Reduction
ü@
3-1 Background and Policy
We at the Asian Disaster Reduction Center are helping member countries develop disaster-reduction systems by collecting information on natural disasters, as well as keeping a record of their disaster management laws, plans and concrete measures and putting them onto a database to enable them to be shared with others, and are developing fundamental information infrastructures with which to promote cooperation on a multinational scale concerning disaster reduction.
In fiscal 1998, we got a grip on the outline of the following by gathering and storing in the database information from existing materials, contact persons in each country and other disaster-reduction-related organizations, and started disseminating the following information:
(1) Disaster-reduction systems (judicial system, organization, basic plans, disaster management manuals, etc.);
(2) Actual cases of disaster countermeasures (measures taken during great natural disasters in the past, such as the Great Hanshin-Awaji Earthquake);
(3) Natural disaster information (descriptions and damage incurred by earthquakes, floods and other natural disasters in the past); and
(4) Human resources information (persons of learning and experience, etc.).
Prior to our collection of data, we carried out investigations into disaster-reduction-related home pages on the Internet, with a view to establishing collaboration and cooperation with other organizations.
Table 3-1-1 Disaster Information on the Internet
< Entire table
üĘhttps://www.adrc.asia/annual/98/H3-1-3-1eg.xls>|
General ü@Disaster |
Earth quakes |
Tsunami |
Volcano |
Hurricane Typhoon |
Flood |
||||
|
OCHA(United Nations Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs üj |
OCHA(Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs üj |
UN |
üŤ |
ReliefWeb üi Menu:Natural Disasters, andSearch engine üj |
|||||
|
IDNDR(International Decade for Natural Disaster Reduction) |
RADIUS |
Switzerland |
ü~ |
üŤ |
ü~ |
ü~ |
ü~ |
ü~ |
ü~ |
|
IFRC üĽ RCS (International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies) |
IFRC üiInternational Federation of Red Crescent Societies) |
üŤ |
Direct from the field (the report on the state of the area where disaster happened and the response of IFRC) |
||||||
|
CRED üiUniversite Catholique de Louvainüj |
CRED |
Belgium |
üŤ |
EMDAT |
|||||
|
Institute of Industrial Science ,University of Tokyo |
INCEDE |
Japan |
ü~ |
üŤ |
ü~ |
ü~ |
ü~ |
ü~ |
ü~ |
|
Emergency Management Australia |
EMA üiEmergency Management Australia) |
Australia |
üŤ |
Info çA Emergency Management Projects |
|||||
|
Natural Hazards Research Centre, Macquarie University |
Natural Hazards Research Centre |
Australia |
üŤ |
Natural Hazards Quarterly |
|||||
|
MINISTRY OF CIVIL DEFENCE |
Emergency Management and Civil Defence |
New Zealand |
üŤ |
üŤ |
üŤ |
Some New Zealand Natural Disasters 1840 ü`1980 |
|||
|
Department of Seismology, University of Paris |
GEOSCOPE Network of IPGP |
France |
üŤ |
Seismic data from the 25 stations in the world |
|||||
|
IRIS(Incorporated Research Institutions for Seismology) |
Seismic Monitor |
USA |
üŤ |
Seismic Monitor(location maps of seismic events üj |
|||||
|
The United States Govrment |
FEMA(Federal Emergency Management Agency) |
USA |
üŤ |
üŤ |
üŤ |
üŤ |
üŤ |
üŤ |
Preparedness(risk of the disasters, Preparedness to them) |
|
Earthsat |
EarthSat |
USA |
üŤ |
üŤ |
Area map at risk of flood in US |
||||
|
National hurricane Center( Tropical Prediction Center) |
National Hurricane Center |
USA |
üŤ Hurricanes |
Past Hurricane History in US |
|||||
|
Natural Hazards Centre at the University of Colorado,Boulder |
Natural Hazards Center at the ü@University of Colorado,Boulder |
USA |
üŤ |
Quick Response Reports |
|||||
|
Simon Fraser Univeresity |
Hazard Net |
USA |
üŤ |
üŤ |
üŤ |
üŤ |
üŤ |
Links to various databases, Organisations ü@ü@ü@ü@ü@ü@ü@ü@ü@ü@ü@ü@ü@ü@ü@ü@ |
|
|
NOAA üENational Weather Service,The Office of Hydrology |
NOAA üENational Weather Service |
USA |
üŤ |
River Conditions in the United States |
|||||
|
NASA |
VOLCANO WORLD |
USA |
üŤ |
Volcanos of the World |
|||||
|
Institute for Astronomy University of Hawaii üiIndividual:Thomas R. Metcalfüj |
Tropical Storms, Worldwide |
USA |
üŤ Hurricanes |
Tropical Storms, Worldwide |
|||||
|
GeoHazards International |
GEOHAZARDS INTERNATIONAL |
USA |
ü~ |
üŤ |
ü~ |
||||
|
Natural Museum of Natural History(Smithsonian Institution) |
Global Volcanism Program |
USA |
üŤ |
Holocene Volcano Basic Data |
|||||
|
NGDC (National Geophysical Data Center) |
Natural Hazards Data Available Online |
USA |
üŤ |
üŤ |
üŤ |
Natural Hazards Data available on line |
|||
ü@
Table 3-1-3-2 Home Page of ADRC Member Countries
< Entire table
üĘhttps://www.adrc.asia/annual98/h3-1-3-2eg.xls>| Country |
The address of homepages of Govenments* |
Information on the disaster |
Info. on disaster peparedness |
Information on responses to disasters |
|
|
Disaster Countermeasures |
Response to Disasters |
||||
|
Bangladesh |
Government of the People's Republic of Bangladesh http://bangladeshoneline.com/gob/ |
üŤüi only on the Flood in 1998) |
ü~ |
üŤ (as the left cell states) |
üŤ (as the left cell states) |
|
Cambodia |
ü~ |
ü~ |
ü~ |
ü~ |
ü~ |
|
China |
National Meteorological Center http://www.nmc.gov.cn/ |
ü~ |
ü~ |
ü~ |
ü~ |
|
India |
Ministry of External Affairs ü@http://www.indiagov.org |
üó ("News" providing the information issued by the government.Search engine by the date of issue for 1998&99üj |
ü~ |
üó (as the left cell states) |
üó (as the left cell states) |
|
Indonesia |
House of People's Representatives, Parliament of Indonesia http://www.dpr.go.id |
üH |
ü~ |
||
|
Kazakhstan |
President of Kazakhstan http://www.president.kz/main/mainmenu.asp?lng=en |
üó ("News" providing the information issued by the government.Search engine by the date of issue for 1998&99üj |
ü~ |
üó (as the left cell states) |
üó (as the left cell states) |
|
Laos |
ü~ |
ü~ |
ü~ |
ü~ |
ü~ |
|
Malaysia |
ç@ Ministry of Foreign Affairs http://www.kln.gov.my/ çAMalaysian Meteorological Service http://www.kjc.gov.my/ |
ç@üóüi "Press release" and "News update"providing the current information issued by the Ministry) ü@çAüŤüiMeteorological information and warningüj |
ü~ |
üó (as the left cell states) |
üó (as the left cell states) |
|
Mongolia |
ç@ Government on Mongolia http://www.pmis.gov.mn/MAINPGE/Defengg.htmü@ü@ü@ü@ü@çAMinistry of Defense http://www.pmis.gov.mn/mdef/english/index.htmü@ü@ü@ü@ü@ü@ü@çBMinistry of Nature and Environment http://pmis.gov.mn/env/new.htm |
ç@ ?"Government News"(not found) çAü~ü@ü@ü@ü@ü@ü@ü@ü@ü@ü@ü@ü@ü@ü@ü@ü@ü@çBüóüiThe map of the current state of clouds, snow & fire) |
ü~ |
ç@üH (as the left cell states) çAü~ü@ü@ü@ü@ü@ü@ü@ü@ü@ü@ü@ü@ü@ü@ü@ü@ü@çBü~ |
ç@üH (as the left cell states) çAü~ü@ü@ü@ü@ü@ü@ü@ü@ü@ü@ü@ü@ü@ü@ü@ü@ü@çBü~ |
|
Myanmar |
ü~ (The golden pages of Myanmar, http://www.myanmar.com/) |
ü~ |
ü~ |
ü~ |
ü~ |
|
Nepal |
ü~ |
ü~ |
|||
|
Papua New Guinea |
Prime Minister and National Executive Council ü@http://datec.com.pg/pgsoffice.nsf/pages/home |
üóüi "Media Releases"providing the current information issued by the governmentüj |
ü~ |
üó (as the left cell states) |
üó (as the left cell states) |
|
Philippines |
Office of the Press Secretary http://www.ops.gov.ph/frmail.htm |
üŤüi Search Engine for the news issued by the government in 1997ü`99üj |
ü~ |
ü~ (as the left cell states) |
ü~ (as the left cell states) |
|
Russia |
? |
ü~ |
|||
|
S.Korea |
Ministry of Government Administration and Home Affairs (which Disaster Prevention and Preparedness Bureau belongs to)(No English version) http://www.mogaha.go.kr/htm |
üH(Written in Korean) |
ü~ |
üH |
üH |
|
Singapore |
Ministry of Civil Defence Force http://www.mha.gov.sg/scdf/ |
üóüi "SCDF News-Online"providing the current information issued by the Ministryüj |
ü~ |
üó (as the left cell states) |
üó (as the left cell states) |
|
Sri Lanka |
Ministry of Foreign Affairs http://www.lanka.net/fm/for_1.html |
üóüi "Press release" and "News update"providing the current information issued by the governmentüj |
ü~ |
üó (as the left cell states) |
üó (as the left cell states) |
|
Tadzhikistan |
ü~ |
ü~ |
ü~ |
ü~ |
ü~ |
|
Thailand |
The Secretariat of the Prime Minister, Spokesman Bureau http://spokesman.go.th/index/press.htm |
üóüi "Press Releases"providing the current information issued by the Bureauüj |
ü~ |
üó (as the left cell states) |
üó (as the left cell states) |
|
Uzbekistan |
InfoCentre of the Office of the President of the Republic of Uzbekistan (Mass Media- Official news) http://uzinfo.uzpak.uz/massnedi.html |
üóüi "Official News" providing the current information issued by the governmentüj |
ü~ |
üó (as the left cell states) |
üó (as the left cell states) |
|
Vietnam |
Disaster Manegement Unit(DMU) (Project of government and UNDP) http://www.undp.org.vn/dum/dum/en/intro.htm |
üŤ (natural disaster information) |
üŤüi Flood-control measure and a degree of lawüj |
üóüi there is a link to the United Nations, IFRC, and so onüj |
üóüi there is a link to the United Nations, IFRC, and so onüj |
|
* The Ministries and Departments assumed to be related to Disaster information or to issue such information |
|||||
|
üŤüF there is a specific way to obtain the information on natural disasters |
|||||
|
üóüF it is likely to include the information on natural disasters |
|||||
ü@
3-2 Information on Disaster-reduction Systems
3-2-1 Information on Disaster-reduction Systems Gathered by the Center
Information on disaster-reduction systems ranges from judicial systems, disaster management organizations and disaster-reduction basic plans to disaster-reduction measures manuals for each country. In fiscal 1998, we aggressively gathered information from existing materials, member countries, field investigations and the International Experts' Meeting.
(See https://www.adrc.asia/nations/)
1) Legal System of the ADRC Member/Advisory Countries
Below are brief descriptions of the legal system of the ADRC member/advisory countries.
| Country |
Descriptions |
|
Bangladesh |
Disaster Management Law under deliberation. Waiting for government approval |
|
Cambodia |
Civil Defense Act passed in 1993 |
|
India |
Natural disasters are dealt with at the national, district and sub-district levels |
|
Indonesia |
Presidential Decree No. 43/1990(1995) |
|
Japan |
Disaster Countermeasures Basic Act, passed in 1961 |
|
Kazakhstan |
Law on Civil Defense, Law on Emergency Situations of a Natural and Technological Character, Law on Fire Safety, Law on the Emergency Rescue Services and the Status of Rescuers, Law on National Safety in the Republic Kazakhstan, Law on the Health and (Epidemiological) Welfare of the Population, etc. |
|
Korea |
Civil Defence Act of 1975 is the basic legislation for managing disasters. This act covers war, natural and man-made disasters. For natural disasters, Storm and Flood Disaster Act of 1967 was revised as Natural Disaster Countermeasures Act of 1995. Others include Agriculture and Fishery Disaster Countermeasures Act, Disaster Relief Act, River Act, etc. For man-made disasters, there are Disaster Management Act, Forest Act, Public Road Act, etc. |
|
Nepal |
Natural Disaster Relief Act, formulated in 1982, and amended in 1989 and 1992 |
|
Malaysia |
National Security Council Directive No. 20 |
|
Mongolia |
Civil Defense Law, passed in 1995, only. Applies to both man-made and natural disasters |
|
Papua New Guinea |
Disaster Management Act, passed in 1975. Currently studying equivalent acts for provincial and local governments |
|
Philippines |
Presidential Decree No. 1566, promulgated in 1978 |
|
Russia |
1)Law on Protection and Territories against Disasters of Natural and Technological Origin, (2) Law on Disaster Relief, (3) Law on Civil Defense, (4) Law on Deliveries for the Federal State Needs, (5) Law on State Reserves of Material Assets for Response to Disasters |
|
Singapore |
Civil Defense Act of 1986 |
|
Sri Lanka |
Disaster Countermeasures Bill under deliberation |
|
Tadzhikistan |
Civil Defense Act, passed in 1996 |
|
Thailand |
Civil Defense Act, passed in 1979 |
|
Uzbekistan |
Law on Protection of the population against acts of nature and technological accidents, formulated in 1998 |
|
Vietnam |
Prime Minister's Directives and Political Bureau's announcements |
|
Australia |
6 out of 8 States and Territories have disaster management legislation. |
|
Switzerland |
Civil Defence Law, Federal Law of 1976 concerning International Development Cooperation and Humanitarian Aid |
2) Disaster Management Organizations of the Member and Advisory Countries.
Below are brief descriptions of the disaster management organizations of the member and advisory countries.
| Country |
Descriptions |
|
Bangladesh |
Has a Ministry of Disaster Management and Relief, which coordinates different government agencies, as well as the National Disaster Management Council (headed by the Prime Minister), an Inter-Ministerial Disaster Management Co-ordination Committee, and a Cyclone Preparedness Programme Implementation Board |
|
Cambodia |
Disaster management policy formulated in 1995 with the establishment of the National Committee for Disaster Management, which consists of 16 cabinet members, is supervised by the Prime Minister, and is fully supported by the Cambodian Red Cross |
|
India |
In ordinary times: Crisis Management Group (headed by the Cabinet Secretary). Natural disasters are taken charge of by the Ministry of Agriculture with support from other ministries. At the state level, the Relief and Rehabilitation Department or the Department of Revenue, and on the district level, the District Level Coordination and Review Committee (chaired by the Collector), are responsible for administrative response. In the event of disaster: the Multi-disciplinary Central Government Team offers assistance to affected States |
|
Indonesia |
The National Natural Disaster Management Coordinating Board (Bakornas PB) is responsible for overall coordination for disaster management, with the Coordinating Minister for People's Welfare and Poverty Alleviation serving as a secretariat. Consisting of the Agency for the Assessment and Application of Technology, the Ministry of Public Works, the Meteorological and Geophysical Agency, the Environmental Agency and others, the Board deals with any type of disaster and advises ministries. |
|
Japan |
The Central Disaster Prevention Council (consisting of cabinet members and chaired by the Prime Minister) formulates the Basic Plan for Disaster Prevention. The National Land Agency serves as the secretariat. Specific policies are formulated by ministries and agencies concerned. Main responsibility for local governments is rescue activities under the supervision of the Ministry of Home Affairs. |
|
Kazakhstan |
The Agency for Emergencies is in charge of disaster management through cooperation with City Departments, the Civil Defense Division, the Centre for Emergency Medicine, the Republican Emergency Rescue Unit, the Water Rescue Service and other local bodies. The Prime Minister heads the civil defense of the country. |
|
Korea |
Chain of command for disaster mitigation: President -> Prime Minister -> Ministry of Government Administration and Home Affairs -> Civil Defense and Disaster Management HQ, under which are placed the Disaster Prevention and Preparedness Bureau (on the basis of the Natural Disaster Countermeasures Act), the Civil Defense and Disaster Management Bureau and the Fire Administration Bureau (ditto). At the district level, local governments are in charge. |
|
Nepal |
The Central Natural Disaster Relief Committee commands the Regional Natural Disaster Relief Committee, the District Natural Disaster Relief Committee, the Local Natural Disaster Relief Committee, the Relief and Treatment Sub-Committee and the Supply, Shelter and Rehabilitation Sub-Committee. The Natural Disaster Relief Section of the Ministry of Home Affairs is responsible for the formulation of national disaster management policies, preparedness for disasters, rescue operations, data collection, and distribution of funds to victims. Has a nationwide disaster management network. Coping with disasters in remote areas needs to be considered. |
|
Lao PDR |
The Ministry of Welfare serves as a secretariat for the Prime Minister's Department. |
|
Malaysia |
Under National Security Council Directive No. 20, the National Security Division in the Prime Minister's Department is responsible for coordination. The Disaster Management and Relief Committee formulates and implements specific action plans. Disaster management is carried out at the federal, state and district levels. |
|
Mongolia |
In addition to the Ministry of Nature and Environment (formulating policy) and the State Civil Defense Department (carrying out day-to-day operations), the State Permanent Emergency Commission (consisting of cabinet members and chaired by the Prime Minister) is convened when a disaster occurs. District commissions are also convened. |
|
Papua New Guinea |
The National Disaster and Emergency Services were established by the Disaster Management Act. The National Disaster Committee declares a state of disaster and recommends action plans to the Government. Each province has a Provincial Disaster Committee. |
|
Philippines |
The National Disaster Coordination Council formulates disaster management plans and takes emergency and rehabilitation measures through cooperation with the private sector. Consisting of heads of 14 national ministries, the Chief of Staff of the Armed Forces of the Philippines, the Secretary-General of the Philippine National Red Cross, the Administrator of the Defense Ministry's Office of Civil Defense and others, the committee designs solutions and advises the President if a state of emergency is announced. |
|
Russia |
Has a Ministry of the Russian Federation for Civil Defense, Emergencies and Elimination of Consequences of Natural Disasters, which, unlike similar organizations in other countries, has its own personnel and resources. |
|
Singapore |
The Ministry of Home Affairs is responsible for disaster management. The Civil Defence Force and Police Force are responsible for implementing various activities. The Disaster Management Committee is convened when a large-scale disaster occurs. |
|
Sri Lanka |
The Ministry of Social Services set up a National Centre for Disaster Management. A framework for disaster management not yet in place at the provincial and district levels. |
|
Tadzhikistan |
Prime Minister oversees disaster reduction and countermeasures. The Committee for Emergencies and Civil Defense of the Government of Tajikistan plays a coordinating role. Each province and district has its own committee and Civil Defense Headquarters. |
|
Thailand |
The National Civil Defence Committee (chaired by the Interior Minister) was established under the Civil Defence Act of 1979. Consisting of 17 representatives from ministries concerned, including the Defence Ministry, Agriculture and Cooperative Ministry and the Public Health Ministry, the committee coordinates civil defence measures and policies. NGOs offer assistance at the regional and local levels. |
|
Uzbekistan |
Five members of the Department of Emergency Situations, the Cabinet Ministry of Uzbekistan coordinate governmental ministries and disaster countermeasures. |
|
Viet-nam |
The Central Committee for Flood and Storm Control is responsible for disaster management through cooperation with the Provincial People's Committees and Army Headquarters. The National Centre for Hydro-Meteorological Forecasting issues early warnings against natural disasters. |
|
Australia |
Each State and Territory has its own emergency management committee. Local committees, regional committees, Emergency Management Australia and the National Emergency Management Committee deal with disasters in the order named. When occasion demands, a Federal Emergency Management Special Committee is organized to play a coordinating role at the state level. |
|
New Zealand |
Currently reconstructing emergency management arrangements based on a risk management plan. |
|
Switzerland |
Switzerland: Responsibility for emergency management rests mainly with local governments. District authorities take leadership when a disaster occurs. On the federal level, the Ministry of Defense has jurisdiction over disaster management |
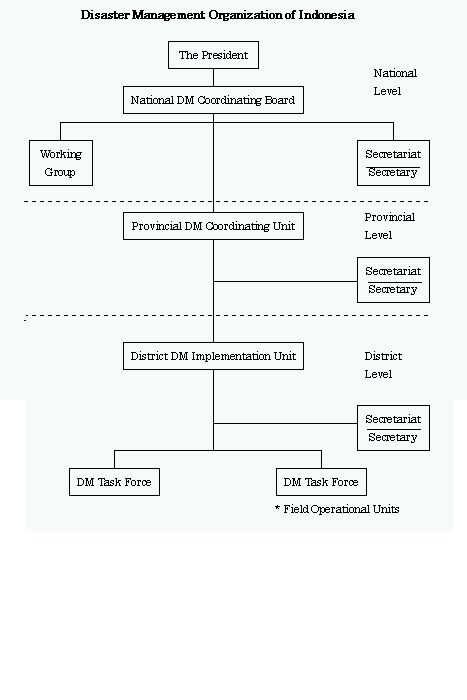
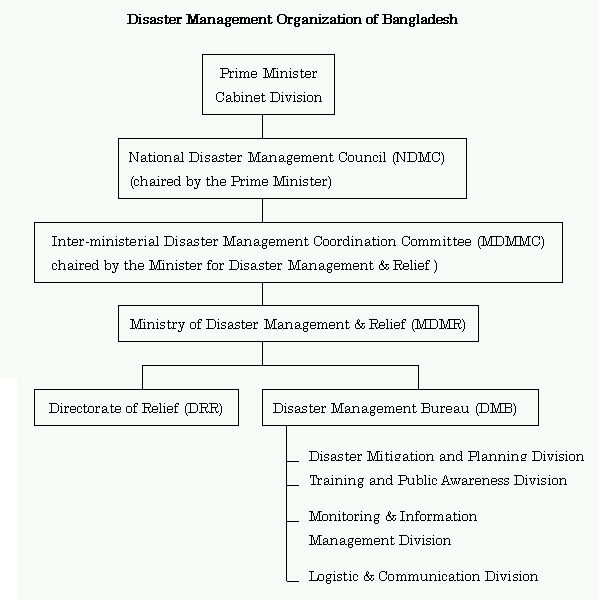
Shown below are two different models of a disaster management organization. The first (Indonesia) features a cross-ministerial organization (National DM Coordinating Board), whereas the second features a ministry specializing in disaster management (Ministry of Disaster Management & Relief).
(1) Indonesia

(2) Bangladesh
3) Basic Plans for Disaster Management of the Member and Advisory Countries
Below are brief descriptions of the basic plans for disaster management of the member and advisory countries.
| Country |
Descriptions |
|
Bangladesh |
No basic plans, but disaster countermeasure bylaws apply to each ministry and agency, in accordance with which state, local and village disaster management committees are constituted. Bangladesh hopes to formulate a disaster countermeasures plan by June 1999. Only one disaster management manual is available, mainly for man-made disasters, prepared by civic organizations. |
|
Cambodia |
Disaster Management Act under preparation at the state level. Also formulating plans to foster leadership, build manpower and expand financial resources at the district level. Formulating provisional plans for relief activities and training. |
|
India |
Links disaster mitigation plans with the Vision 2020 development plan to incorporate the latest information technology, insurance and legal support. |
|
Indonesia |
With support from UNDP, has completed a Disaster Information System, which includes a disaster management GIS system and a disaster and rescue information database. |
|
Japan |
In accordance with the Disaster Countermeasures Basic Act, the Central Disaster Prevention Council approves basic plans for disaster prevention, which stipulate prevention, initial response and reconstruction for 4 categories of natural disasters and 8 categories of man-made disasters (fires, train accidents, etc.). Revised in '95 and '97 after the Great Hanshin-Awaji Earthquake, the plans also lay down the specific responsibilities of each ministry and agency, enterprises, municipal governments, volunteers and public service corporations. |
|
Kazakhstan |
The Agency for Emergencies is formulating disaster management emergency action plans in line with principles set within the framework of IDNDR. Formulation of a comprehensive Kazakhstan natural Disaster Preparedness Plan started. |
|
Korea |
Has disaster management programs, reserve plans and civil defense plans (for the Red Cross, volunteers, etc.). Approx. 42,000 people were educated from March to May 1998, and the government carried out exercises under computer-simulated typhoon conditions. As part of their Basic Five-Year Disaster Prevention Plan (1997 - 2001/Budget: U.S. $22 bn.), the government invested U.S. $4 billion in 22 key items from disaster countermeasures to technical development. |
|
Nepal |
The 9th Plan (1998 - 2002) underlines the need to strengthen the national disaster management system and fire fighting capability through more advanced technology. The National Committee for IDNDR formulates the National Action Plan. Has prepared a National Comprehensive Plan on Disaster Management in cooperation with UNDP and other organizations. |
|
Lao PDR |
(1) Development of disaster preparedness act and action plan, (2) Human development plan, (3) Improved communications system, (4) Secure financial sources, and (5) Early warning system |
|
Malaysia |
Formulating its own plan, modelled after the Indonesian plan, which includes mid- and long-term perspectives and requests for technical support. Also formulating forest fire fighting plan through cooperation with Australia, which stipulates the roles of ministries and agencies concerned and actions to be taken for each of the four individual cases including industrial disasters and landslides. |
|
Mongolia |
Drafting a natural disaster mitigation action plan. Civil defense forces have manuals. |
|
Papua New Guinea |
(1) District disaster management plan (for small-scale disasters that are taken care of by provincial authorities), (2) National Disaster Management Plan (under review). Ministry of Industry formulates plans for each category of disasters (oil spills, plane crashes, fires, etc.), which are reviewed by the ministries and agencies concerned every quarter. |
|
Philippines |
The Government and each ministry have and review their disaster management plans on a regular basis. |
|
Russia |
The Government formulates a basic plan for disaster management, which stipulates the roles of ministries and agencies concerned for disaster reduction, relief and rehabilitation. The Disaster Preparedness Plan stipulates a plan for each category of disaster, such as forest fires, earthquakes and floods. Depending on the scale of the disaster, either central or local authorities implement response strategies in accordance with the plan. No federal manual available. |
|
Singapore |
Has an executive group plan, which responds to any kind of disasters and consists of 16 specific action plans (train accidents, explosions, chemical disasters, tunnel disasters, plane accidents, etc.) |
|
Sri Lanka |
Formulated its Basic Plan for Disaster Countermeasures in 1990. Currently considering revising the plan. No manual for countermeasures. |
|
Tajikistan |
Every year, the Government adopts an annual civil defense plan, which describes geographical conditions and disaster preparedness plans for local governments. One of the biggest natural disasters in the territory of Tajikistan was an earthquake in 1911. Held a disaster management meeting in May 1999. |
|
Thailand |
Thailand: A typhoon in 1988 made the Government recognize the importance of disaster countermeasures, leading to inclusion of the Disaster Countermeasures 5-Year Plan (1997 - 2001) in the National Development Plan. Based on the plan, the Civil Defense Master Plan was introduced in 1998, which defines the responsibilities of ministries and agencies concerned at times of disaster, and stipulates inter-ministerial disaster cooperative setups, efficient communications and cooperation with NGOs. Currently evaluating its effect over the last 6-7 months (as of Febrary 1999). |
|
Uzbekistan |
A 1997 flood in Kyrgyz Republic took 116 lives. Needs a satellite early warning system. |
|
Viet Nam |
The Department of Dyke Management & Flood Control, Ministry of Agriculture & Rural Development, plans to formulate a disaster management action plan up to 2010. |
|
Australia |
All States and Territories have a disaster reduction plan and support plan, which stipulates the provision of support for overseas disasters. The Australia Emergency Management Manual Series covers most of the necessary responses. |
|
Switzerland |
Basic plan for domestic disaster management in place under the Ministry of Defense (includes terms and definitions for unified understanding of central and local governments). Has by-disaster-type plan for day-to-day operation. International cooperation in strategic responses to natural disaster management, which are under the jurisdiction of the Ministry of Foreign Affairs. |
ü@
3-2-2 Future Policy
In fiscal 1998, we mainly gathered information on the disaster management systems of the member and advisory countries. Our next task is to analyze and put the information into a database, and gain an understanding of each country's specific needs, while continuing to accumulate detailed information on legislative systems including laws, regulations and orders, as well as on disaster management policies and plans, such as governmental policies, basic plans, countermeasures and manuals.
We at the Asian Disaster Reduction Center are determined to continue contributing to improvements in member and advisory countries' disaster management systems by providing the above information.
ü@
3-3 Cases of Disaster Counter Measures
3-3-1 Accumulated Cases of Disaster Reduction Measures
To secure a good understanding of the basics of how Asian countries and concerned organizations have dealt with disasters in the past, we have gathered information from materials issued by member countries, research institutes around the world and other organizations, as well as information on the Great Hanshin-Awaji Earthquake, which inflicted the greatest economic damage for a single disaster, and categorized them.
1) Cases of Disaster Counter Measure by Member Countries
After a disaster occurs, OCHA Situation Reports, which summarize the extent of damage and how it is dealt with, are made available on the Internet via the relief web of the United Nations Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs (UN-OCHA).
We selected and developed a database comprised of cases of disaster counter measures from information posted on the relief web, country reports that member countries provided to the Center, and other databases.
(Excerpts shown in Table 3-3-1-1. The entire table can be found at
https://www.adrc.asia/annual98/h3-3-1-1eg.xls)Table 3-3-1-1 Cases of Counter Measures against Natural Disasters <1998> (Excerpts)
< Entire table
üĘhttps://www.adrc.asia/annual98/h3-3-1-1eg.xls>| Country |
Disaster |
Date |
Source |
Report |
Date of Issue |
The outlines of the case against disaster |
|
China |
Flood |
Jun-98 |
OCHA |
China - Floods OCHA Situation Report No. 1 |
9-Jun-98 |
The governments dispatched task forces to the areas to coordinate the relief materials were distributed ,and to treat the victims and to prevent the occurrence of epidemics.Authorities are organizing repair of damaged infrastructure facilities. |
|
OCHA |
China - Floods OCHA Situation Report No. 3 |
3-Jul-98 |
The Ministry of Civil Affairs allocated 100 million RMB(approximately USD 12.1 million) and delivered 2,200 tents to the disaster areas, as well as assessment and relief teams. |
|||
|
OCHA |
China - Floods OCHA Situation Report No. 4 |
15-Jul-98 |
Sichuan provincial government has allocated USD 3,627,570 for emergency flood prevention and disaster relief. At present, the social situation is stable, and relief activities and productions in the disaster stricken areas are running in order. |
|||
|
OCHA |
China - Floods OCHA Situation Report No. 7 |
21-Aug-98 |
The Government has provided relief funds and large quantities of relief materials. People's Liberation Army personnel and others are currently deployed to fight floodwaters. |
|||
|
China |
Flood |
Jun-98 |
OCHA |
China - Floods OCHA Situation Report No. 8 |
3-Sep-98 |
The Government departments concerned dispatched to the disaster areas more than 100 working teams. The Army, military police, public security troops and militia played an important role in rescue. |
|
Bangladesh |
Flood |
Jul-98 |
OCHA |
Bangladesh - Floods OCHA Situation Report No. 1 |
17-Jul-98 |
The Emergency Control Room (ECR) are in the process of compiling the information of the affected districts. The district administrations have begun emergency relief operations where necessary. |
|
OCHA |
United Nations Flash Appeal in support of the Government of Bangladesh for Relief to the Victims of the Floods in Bangladesh |
4-Sep-98 |
The Government of Bangladesh has mobilized all resources and personnel to mitigate the suffering of the victims ,and has distributed cash from the Prime Minister's relief fund ,and has distributed rice,biscuit,saris,lunghis,old clothing and medicalteams. |
|||
|
Bangladesh |
Country Report(1998) |
The Bangladesh government properly evacuated isolated inhabitants and kept watch on the situation of the flood with the maximum attension, so the number of the dead was minimum for the large disaster. |
||||
|
Indonesia |
Volcanic eruption |
Jul-98 |
OCHA |
Indonesia - Volcanic eruption OCHA Situation Report No.1 |
15-Jul-98 |
The provincial administration has sent relief teams, including medical workers, to the affected areas. |
|
Papua New Guinea |
Tsunami |
Jul-98 |
IFRC |
Papua New Guinea:Tidal Wave Information Bulletin No. 1 |
18-Jul-98 |
Rescue teams from the capital, Port Moresby, have been despatched. Helicopters are being used to search for survivors and food shipments are on the way, according to the Government's National Disaster Centre. |
|
OCHA |
Papua New Guinea - Tsunami OCHA Situation Report No. 4 |
21-Jul-98 |
Both public hospitals in Vanimo and Wewak are coping well with the influx of injured. In addition to treatment of the injured, priorities now are shifting to the location and burial of the dead, shelter of the homeless and resettlement. |
ü@
2) The Great Hanshin-Awaji Earthquake
With a view to sharing with the global population the lessons learned from this terrible earthquake, we constructed on our web site the "Great Hanshin-Awaji Earthquake Database (on full-text basis)," which is linked to other information accessible on the Internet. At the time of writing, 219 pieces of Japanese data and 82 in English are available from our home page (https://www.adrc.asia/hanshin/database/).
We also excerpted descriptions of the Great Hanshin-Awaji Earthquake from the 1995 through 1998 issues of the Government's Disaster Prevention White Paper, which serves as an official record in Japan of the quake, and posted them on our home page in both Japanese and English.
(Disaster Prevention White Paper:
https://www.adrc.asia/hanshin/hakusho/default.asp)ü@
3-3-2 Future Policy
We will select cases of large-scale disaster reduction measures in member countries in the past, ask them to provide us with information on these cases and accumulate them in our database of natural disaster, which we will continue to develop in a systematic manner.
We will also keep track of new entries of information on the Great Hanshin-Awaji Earthquake to the Internet, ask existing link
üfs owner and others for the provision of information to further expand the database (link page) and continue to translate some Japanese information into English.Table 3-3-2-1 Database of the Great Hanshin-Awaji Earthquake
(Excerpts)
<Entire table
üĘ https://www.adrc.asia/hanshin/default.asp?lang=en>| Top Page |
Title-1 |
Title-2 |
Title- éR |
Author |
DESCRIPTION |
|
Hyogo Prefecture |
Fire & Disaster Management Div. |
Outline of the Earthquake |
Hyogo Prefecture |
The Great Hanshin-Awaji Earthquake: the Experience and Reconstruction |
|
|
Hyogo Prefecture |
Outline of the Great Hanshin-Awaji Earthquake Reconstruction Plan (Phoenix Plan) |
Hyogo Prefecture |
|||
|
City of Kobe |
The Great Hanshin-Awaji Earthquake Statistics and Restoration Progress |
City of Kobe |
Official Report /City of Kobe |
||
|
City of Kobe |
The Disaster of KOBE City |
City of Kobe |
|||
|
Kobe City Board of Education |
100 days after The Great Hansin Earthquake - Education in Kobe City |
Kobe City Earthquake Relief Headquarters: School Affairs |
|||
|
United Nations Centre for Regional Development (UNCRD) |
Comprehensive Study of the Great Hanshin Earthquake |
UNCRD Research Report Series No.12 |
United Nations Centre for Regional Development (UNCRD) |
Comprehensive report (Retyped by ADRC) |
|
|
ROKKO I-NET NEWS |
Rokko Sabo Work Office, Kinki Regional Construction Bureau, Ministry of Construction |
THE HYOGO SOUTH GREAT EARTHQUAKE AND SABO |
|||
|
OKLAHOMA GEOLOGICAL SURVEY |
SEISMOGRAMS AND SPECTROGRAMS |
Seismogram: 1995 Jan 16, Kobe, Japan |
Oklahoma Geological Survey |
Seismogram graphical data with a few lines of description. |
|
|
USGS |
ARCHIVES & RESEARCH,RESEARCH & PUBLICATIONS |
"Slip History Of The Kobe, Earthquake |
David J. WALD |
8 page academic paper on the tectonic content of the Kobe EQ |
|
|
USGS / WESTERN REGION GEOLOGIC INFO SERVER |
EARTH-SCIENCE INFORMATION |
OTHER REGIONS EARTH SCIENCE DATASETS |
Preliminary Map Of Peak Horizontal Ground Acceleration |
U.S. Geological Survey |
2 page report with map showing the EQ spread around Kansai |
|
USGS EARTHQUAKE INFORMATION |
STUDYING EARTHQUAKES |
Use of Fault striations and dislocation models to infer tectonic shear stress |
U.S. Geological Survey |
Report about Rokko and Nojima fault causes of the Kobe EQ |
|
|
USGS EARTHQUAKE INFORMATION |
Tectonic Setting of the Kobe Earthquake. A geological map. |
U.S. Geological Survey |
1 page map of Japan showing Kobe EQ compared to other quakes around the country |
||
|
USGS EARTHQUAKE INFORMATION |
'Kobe Earthquake was Deadliest, but not largest in '95' |
U.S. Geological Survey |
2 page report about 25 big quakes in 1995 around the world |
||
|
GLOBAL EARTHQUAKE RESPONSE CENTER |
EARTHQUAKE LINKS-SPECIFIC EARTHQUAKES |
Kobe map of fault line |
The Global Earthquake Response Center |
Map of fault line through Kobe |
|
|
GLOBAL EARTHQUAKE RESPONSE CENTER |
EARTHQUAKE LINKS-SPECIFIC EARTHQUAKES |
Kobe map of fire damage |
The Global Earthquake Response Center |
Map of fire damage in Kobe |
|
|
GLOBAL EARTHQUAKE RESPONSE CENTER |
EARTHQUAKE LINKS-SPECIFIC EARTHQUAKES |
Kobe photos gathered by USGS Menlo Park CA |
The Global Earthquake Response Center |
photographs in jpeg format |
|
|
GEOSCIENCES: NSF DIRECTORATE FOR THE GEOSCIENCES |
ABOUT GEO / NEWS STORIES AND PRESS RELEASES |
NSF PR 95-12 February 23, 1995 |
Modern Buildings fared well in the Kobe Quake |
National Science Foundation |
Discussion about the stronger Kobe buildings |
|
TURNER-FAIRBANK HIGHWAY RESEARCH CENTER |
PUBLIC ROADS |
ARCHIVE |
Aftermath of the Kobe Earthquake |
Turner-Fairbank Highway Research Center |
Report about roads and bridges after the quake. |
|
TURNER-FAIRBANK HIGHWAY RESEARCH CENTER |
PUBLIC ROADS |
ARCHIVE |
Lessons from the Kobe Quake |
Turner-Fairbank Highway Research Center |
Report about roads and bridges after the quake. |
|
WESTERN STATES SEISMIC POLICY COUNCIL (WSSPC) |
EARTHQUAKE RESOURCES |
Index of Kobe Images |
Western States Seismic Policy Council |
40 thumbnail images of Kobe EQ |
|
ü@
ü@
3-4 Information on Natural Disasters
3-4-1 Information on Natural Disasters Gathered by the Center
We accumulated basic materials with which to build a new database of information concerning natural disasters. The database allows various types of information to be easily obtained on past disasters by combining in an organic manner on our home page a wide range of information on natural disasters in the past made available by different institutes.
To survey occurrences of past natural disasters in member countries, we sought out the Emergency Disaster Events Database (EMDAT) of the Center for Research on the Epidemiology of Disasters, Catholic University of Louvain, Belgium (CRED), to provide us with information. (Table 3-4-1-1)
While the EMDAT consists mainly of statistical data, the data stored in the Relief Web covers details and the background of disasters and countermeasures taken inside and out of the country. Because of this, we made a list of locations for information on past disasters on the Internet by integrating the EMDAT with the Relief Web and database of governments, research institutes and universities, as well as summaries of country reports. (Table 3-4-1-2)
In addition, after discussions at the ADRC First International Expert Meeting in February 1999, we prepared a draft format that covers all the items necessary to compile data on past disasters. (Table 3-4-1-3)
Table 3-4-1-1 Natural Disasters in Member Countries
<1900 - 1998><ADRC Member Countries>
ü@ü@ü@ü@<https://www.adrc.asia/annual98/h3-4-1-1.xls>| Country |
Number of Disasters |
Dead ç@ |
Injured |
Affected Population çA |
Homeless |
Amount of Damage (US$) |
ç@ /çA |
||
|
Dead;10-99 |
100-999 |
Over 1000 |
|||||||
|
Bangladesh |
74 |
62 |
27 |
2,571,744 |
845,006 |
362,270,426 |
41,810,667 |
9,024,279,000 |
0.71% |
|
Cambodia |
1 |
2 |
665 |
7,850,000 |
29,100 |
3,542,000 |
0.01% |
||
|
China |
136 |
96 |
46 |
11,829,273 |
647,641 |
1,119,679,656 |
31,504,490 |
162,638,015,000 |
1.06% |
|
India |
124 |
156 |
86 |
1,817,013 |
35,602 |
1,796,380,834 |
23,674,100 |
28,887,161,000 |
0.10% |
|
Indonesia |
78 |
43 |
11 |
57,613 |
272,122 |
10,572,436 |
773,028 |
18,429,556,000 |
0.54% |
|
Japan |
105 |
50 |
25 |
220,779 |
35,957 |
7,639,217 |
1,705,100 |
165,332,600,000 |
2.89% |
|
Kazakhstan |
1 |
1 |
121 |
638,000 |
8,000 |
31,775,000 |
0.02% |
||
|
Rep of Korea |
34 |
25 |
1 |
8,217 |
3,366 |
7,571,945 |
1,002,601 |
4,040,554,000 |
0.11% |
|
Laos |
6 |
1 |
431 |
372 |
5,699,400 |
17,600 |
345,559,000 |
0.01% |
|
|
Malaysia |
10 |
1 |
559 |
24 |
815,009 |
23,000 |
75,100,000 |
0.07% |
|
|
Mongolia |
4 |
1 |
1,360 |
61 |
355,000 |
20,000 |
1,847,800,000 |
0.38% |
|
|
Myanmar |
11 |
7 |
3 |
7,630 |
200 |
6,680,540 |
757,939 |
566,615,000 |
0.11% |
|
Nepal |
19 |
19 |
3 |
17,146 |
7,088 |
7,026,525 |
96,350 |
580,613,000 |
0.24% |
|
éoéméf |
13 |
4 |
3 |
9,858 |
947 |
1,563,299 |
121,500 |
452,275,000 |
0.63% |
|
Philippines |
151 |
84 |
12 |
61,578 |
41,262 |
68,732,385 |
9,199,354 |
7,737,068,000 |
0.09% |
|
Russia |
34 |
12 |
10 |
*** |
16,980 |
6,454,295 |
633,369 |
94,517,500,000 |
*** |
|
Singapore |
|||||||||
|
Sri Lanka |
14 |
5 |
2,099 |
6,000 |
16,486,317 |
2,351,140 |
440,060,000 |
0.01% |
|
|
Tajikistan |
4 |
1 |
1 |
1,714 |
39 |
280,100 |
67,105 |
539,400,000 |
0.61% |
|
Thailand |
19 |
7 |
3,553 |
3,416 |
27,373,807 |
247,140 |
4,231,266,000 |
0.01% |
|
|
Uzbekistan |
1 |
96 |
67,800 |
3,900 |
0.14% |
||||
|
Viet Nam |
38 |
33 |
4 |
23,839 |
66,836 |
46,256,065 |
2,139,239 |
2,128,970,000 |
0.05% |
|
Total |
872 |
614 |
233 |
23,009,917 |
1,982,919 |
3,500,393,056 |
116,184,722 |
501,849,708,000 |
0.66% |
|
üq Advisor Countriesür |
|||||||||
|
Australia |
21 |
2 |
1,583 |
13,539 |
22,930,049 |
12,015 |
18,245,233,000 |
0.01% |
|
|
France |
23 |
1 |
865 |
214 |
849,240 |
200 |
4,044,620,000 |
0.10% |
|
|
New Zealand |
2 |
447 |
39 |
38,716 |
5,600 |
381,500,000 |
1.15% |
||
|
Switzerland |
5 |
1 |
357 |
16 |
2,070 |
1,250,560,000 |
17.25% |
||
|
Total |
49 |
6 |
0 |
3,252 |
13,808 |
23,820,075 |
17,815 |
23,921,913,000 |
0.01% |
This data was made available from the EM-DAT Disaster Database, Centre for Research into the Epidemiology
ü@
Table 3-4-1-2 Locations of Information on Major Natural Disasters in the World <1995 - 1998 Exerpt>
< Entire table
üĘhttps://www.adrc.asia/annual98/h3-4-1-2.xls>| Country |
Disaster |
Date |
Home Page |
|
|
Japan |
Earthquake |
Jan-95 |
ReliefWeb |
|
|
Japan |
Earthquake |
Jan-95 |
ADRC |
|
|
Papua New Guinea |
Tsunami |
Jul-98 |
ReliefWeb |
|
|
Papua New Guinea |
Tsunami |
Jul-98 |
ADRC |
|
|
Papua New Guinea |
Tsunami |
Jul-98 |
Australian Geological Survey Organization |
|
|
Papua New Guinea |
Tsunami |
Jul-98 |
DISASTER RELIEF |
|
|
Papua New Guinea |
Tsunami |
Jul-98 |
IFRC&RCS |
|
|
Papua New Guinea |
Tsunami |
Jul-98 |
JET |
|
|
Papua New Guinea |
Tsunami |
Jul-98 |
NOAA |
|
|
Papua New Guinea |
Tsunami |
Jul-98 |
NVNAD |
|
|
Papua New Guinea |
Tsunami |
Jul-98 |
The AGE online |
|
|
Papua New Guinea |
Tsunami |
Jul-98 |
The USC expedition team |
|
|
Papua New Guinea |
Tsunami |
Jul-98 |
United States Geological Survey |
|
|
Papua New Guinea |
Tsunami |
Jul-98 |
WEST ü@COASTü@&ü@ALASKAü@TSUNAMIü@WARNINGü@CENTERü@Homeü@Page |
|
|
Papua New Guinea |
Tsunami |
Jul-98 |
IFRC&RCS |
|
|
Papua New Guinea |
Tsunami |
Jul-98 |
Machizukuri Planning Institute |
|
|
Papua New Guinea |
Tsunami |
Jul-98 |
BRIAN CASSEY photographer |
|
|
Papua New Guinea |
Tsunami |
Jul-98 |
Center for Tsunami Inundation Mapping Efforts |
|
|
Papua New Guinea |
Tsunami |
Jul-98 |
Japan Meteorological Agency |
|
|
Papua New Guinea |
Tsunami |
Jul-98 |
National Defense Academy (NDA) |
|
|
Papua New Guinea |
Tsunami |
Jul-98 |
NOAA |
|
|
Papua New Guinea |
Tsunami |
Jul-98 |
NTF |
|
|
Papua New Guinea |
Tsunami |
Jul-98 |
OCHA-Online |
|
|
Papua New Guinea |
Tsunami |
Jul-98 |
Siberian Center for Global Catastrophes Computing Center |
|
|
Papua New Guinea |
Tsunami |
Jul-98 |
USGS |
|
|
Papua New Guinea |
Tsunami |
Jul-98 |
VITA |
|
|
Papua New Guinea |
Tsunami |
Jul-98 |
Water Cycle Change and Impacts Laboratory |
|
|
Bangladesh |
Flood |
Aug-98 |
BANGLADESH-FLOOD '98 |
|
|
Bangladesh |
Flood |
Aug-98 |
DISASTER RELIEF |
|
|
India |
Floods and Landslides |
Aug-98 |
ADRC |
|
|
India |
Floods and Landslides |
Aug-98 |
IFRC&RCS |
|
|
India |
Floods and Landslides |
Aug-98 |
OCHA-Online |
|
|
India |
Floods and Landslides |
Aug-98 |
ReliefWeb |
|
|
India |
Floods and Landslides |
Aug-98 |
VITA |
|
|
India |
Floods and Landslides |
Aug-98 |
IFRC&RCS |
|
|
Nepal |
Flood |
Aug-98 |
ADRC (Country Report 1998) |
|
|
Nepal |
Flood |
Aug-98 |
OCHA-Online |
|
|
Nepal |
Flood |
Aug-98 |
ReliefWeb |
|
|
Nepal |
Flood |
Aug-98 |
VITA |
|
|
Rep. of Korea |
Flood |
Aug-98 |
ADRC (Country Report 1998) |
|
|
Rep. of Korea |
Flood |
Aug-98 |
IFRC&RCS |
|
|
Rep. of Korea |
Flood |
Aug-98 |
OCHA-Online |
|
|
Rep. of Korea |
Flood |
Aug-98 |
ReliefWeb |
|
|
Rep. of Korea |
Flood |
Aug-98 |
VITA |
|
|
Russian Federation |
Flood |
Aug-98 |
ADRC |
|
|
Viet Nam |
Drought |
Aug-98 |
VITA |
|
|
Viet Nam |
Drought |
Aug-98 |
ADRC |
|
|
Viet Nam |
Drought |
Aug-98 |
OCHA-Online |
|
|
Viet Nam |
Drought |
Aug-98 |
ReliefWeb |
|
|
Viet Nam |
Drought |
Aug-98 |
UNDP |
|
|
Philippines |
Flood |
Sep-98 |
VITA |
|
|
Russia |
Forest Fires |
Sep-98 |
ADRC |
|
|
Russia |
Forest Fires |
Sep-98 |
IFRC&RCS |
|
|
Russia |
Forest Fires |
Sep-98 |
ReliefWeb |
|
|
Russia |
Forest Fires |
Sep-98 |
OCHA-Online |
|
|
Russia |
Forest Fires |
Sep-98 |
VITA |
|
|
Papua New Guinea |
Volcanic Eruption |
Oct-98 |
VolcanoWorld Starting Points-Univ.of Dakota |
|
|
Bangladesh |
Cyclone |
Nov-98 |
VITA |
|
|
Bangladesh |
Cyclone |
Nov-98 |
ADRC |
|
|
Bangladesh |
Cyclone |
Nov-98 |
DISASTER RELIEF |
|
|
Bangladesh |
Cyclone |
Nov-98 |
OCHA-Online |
|
|
Bangladesh |
Cyclone |
Nov-98 |
ReliefWeb |
|
|
Bangladesh |
Cyclone |
Nov-98 |
VIETNAM WEB |
|
ü@
Table 3-4-1-3 Draft Data Format
| ü@ü@ü@ü@ü@ü@ü@ü@ü@ü@ü@DATA FORMAT | ||
|
COUNTRY |
||
|
LOCATION |
(Village, City, Region, Epicenter-Earthquake) |
|
|
KIND |
(Earthquake,Landslides, Flood, Typhoon,---) |
|
|
NAME |
(Ex. Kobe Earthquake---) |
|
|
DATE |
||
|
OUTLINE |
||
|
Human Life Losses |
||
|
Missing |
||
|
Injured |
||
|
Affected Population |
||
|
Homeless |
Evacuated, Resettled |
|
|
Houses destroyed |
Totally |
|
|
Partially |
||
|
Loss of Cattle |
||
|
Loss of Cattle Sheds |
||
|
Estimated Amount of Damage/Losses |
||
|
Measures, Aid, Contribution |
International |
|
|
National |
||
|
Local |
||
|
Others |
||
|
Recovery |
||
|
Reconstruction |
||
|
Rehabilitation |
||
|
Causes of Disasters |
||
|
International Appeal |
Yes No |
Date, Contents |
|
Miscellaneous/Remarks |
||
ü@
3-4-2 Future Policy
We will ask CRED and others to provide all the statistical data available on major disasters since 1900 and add locations of information on those disasters by countries and organizations concerned to it.
At the same time, while helping member countries develop a home page on disaster-reduction-related information, we will develop a networking system which enables them to provide their own information on disasters, which includes items in the draft data format for information on natural disasters, via their home pages.
ü@
3-5 Risk Assessment/Evaluation
3-5-1 Risk Assessment/Evaluation Methods Gathered by the Center
We gathered risk assessment/evaluation methods from country reports and materials made available through field surveys, as well as regional risk assessment, damage estimation methods, hazard maps and other disaster-specific risk assessment /evaluation methods that are carried out in Japan from past documents. We then sorted out their principles and evaluation and implementation methods.
Listed below are materials taken from country reports and field surveys (Table 3-5-1-1), risk assessment/evaluation methods on the Internet (Table 3-5-1-2) and model cases in Japan (Table 3-5-1-3).
ü@
Table 3-5-1-1 Risk Assessment/Evaluation Methods of Member Countries (from 1998 country reports)
| Republic of Korea |
|
Risk Assessment Evaluation System of Disaster Impact (RAESD) Introduced on October 21, 1996 to protect lives and property downstream. Of the 50 projects deliberated up to August 31, 1998, 37 projects were approved. |
|
Philippines |
|
The Philippine Institute of Volcanology and Seismology (PHIVOLCS) Aiming at preparing a hazard map with which to locate activities of active volcanoes, ash flow and damage-prone areas Volcanic hazards identification and mapping: identification, cataloguing and characterization of volcanic activities and potentially active volcanoes, and mapping of the extent of emplacement, thickness of deposition, stratigraphy and source vents. Anticipates hazards and risks from future eruptive episodes. |
|
Laban La Nina Hazard and risk maps for flood due to the La Nina phenomena, communities and lifelines at risk, capacity and vulnerability assessment, and strategic interventions |
ü@
Table 3-5-3-2 Risk Assessment/Evaluation Methods on the Web
| Disaster |
Source |
Report |
Web Address (report) |
Home Page |
|
Earthquake |
National Land Agency |
Earthquake damage estimation support manual |
National Land Agency home page |
|
|
Earthquake |
National Land Agency |
Earthquake damage estimation support tool |
http://www.nla.go.jp/boushi/manual/index.html |
National Land Agency home page |
|
Earthquake |
Fire Defence Agency, Ministry of Home Affairs |
Re: Development of the simplified earthquake damage estimation system Ver. 2 |
Fire Defence Agency home page |
|
|
Earthquake |
Fire Defence Agency, Ministry of Home Affairs |
Re: Simplified earthquake damage estimation system |
Fire Defence Agency home page |
|
|
Tsunami |
Meteorological Agency |
New tsunami forecast |
http://www.kishou.go.jp/info/981102/tsunami.html |
Meteorological Agency home page |
|
Tsunami |
Fire Defence Agency, Ministry of Home Affairs |
Re: Formulation of "Guide to Enhanced Preparedness against Tsunami in Regional Disaster Reduction Plans" and "Tsunami Damage Estimation Manual" |
Fire Defence Agency home page |
|
|
Volcanic eruption |
Volcanological Society of Japan |
Volcanic disasters and eruption predictions |
http://hakone.eri.u-tokyo.ac.jp/kazan/jishome/koukai98/ida.html |
Volcanological Society of Japan home page |
|
Earthquake |
Institute For Fire Safety & Disaster Preparedness |
Damage estimation |
ü@ |
Fire Defense Science Center home page |
|
Fire Research Institute, Fire Defence Agency, Ministry of Home Affairs |
ü@ |
ü@ |
Fire Research Institute home page ü@ |
|
|
Nuclear Power Engineering Corporation |
ü@ |
ü@ |
NUPEC |
|
ü@
ü@
ü@
ü@
ü@
ü@
ü@
Table 3-5-3-3 Main Risk Assessment/Evaluation Methods in Japan (Excerpts) <
https://www.adrc.asia/annual98/h3-5-3-3.doc>Earthquake
| National Land Agency: |
|
Earthquake damage estimation manual (and earthquake damage estimation support tool) |
|
Fire Defence Agency, Ministry of Home Affairs: |
|
Simplified damage estimation system |
|
Metropolitan Tokyo: |
|
Estimation of damage from vertical-thrust earthquakes in Tokyo |
|
Metropolitan Tokyo: |
|
Estimation of Risk Concerning Earthquakes in Each Region |
2) Tsunami
| Meteorological Agency: |
|
New tsunami forecast and tsunami damage estimation manual |
3) Volcanoes
| National Land Agency: |
|
Guide to preparation of maps forecasting areas vulnerable to volcanic eruption disasters |
|
Mt. Sakurajima Volcanic Eruption Disaster Estimation and Survey Conference: |
|
Map forecasting areas vulnerable to Mt. Sakurajima volcanic eruption disaster |
4) Floods
| Ministry of Construction: |
|
Flood and overflow simulations |
ü@
3-5-2 Future Policy
In fiscal 1998, we mainly gathered risk assessment/evaluation methods in Japan. From now on, we will gather and classify regional risk assessment/evaluation methods in Asian countries and industrialized countries in other parts of the world, examine the merits and demerits of each method, and compare them with their Japanese equivalents.
ü@
ü@
3-6 Human Resources Information
3-6-1 Human Resources Information Gathered by the Center
When it comes to disaster reduction, it is important to form a three-cornered network among researchers, government officials in charge of disaster reduction who make decisions on the basis of knowledge and the technologies provided to them by researchers, and citizens who comply with governmental policies and feed comments back to the administration, so as to facilitate exchanges of information.
To this aim, we have developed a comprehensive database of human resources information that covers learned persons, disaster reduction researchers and engineers, government officials in charge of disaster reduction, experts from disaster-reduction-related NGOs and contact persons at disaster-reduction-related international organizations.
The following were surveyed for each individual.
| Title, Name, Date of birth, Sex |
Place of work, Office address, Country where place of ü@work lies, Office phone number, Office fax number, Office e-mail address, Position, Highest academic degree, Educational institute most recently graduated from, Year of graduation, Linguistic proficiency, Work experience (home), Work experience (overseas), Field of study, Key words, Abstract |
The above information was gathered through registration via e-mail to our home page or via fax or mail.
As shown in Table 3-6-3-1, 1,383 persons from 58 countries have registered. Of the figure, 1,290 are from ADRC member countries.
The information is stored in the Center's database, and can be searched by country, field of study, name, etc.
The accumulated information is provided in two different forms: abbreviated data and detailed data. The former is a list of applicable persons, whereas the latter contains every single piece of information made open concerning a certain individual. Displayed on the abbreviated data list are 8 items only: Name, Place of work, Position, Office address, Office phone number, Office fax number, Office e-mail address and Specialized field. Select a certain person from the list, and detailed information including Highest academic degree, Linguistic proficiency, Work experience (home) and Work experience (overseas) will be provided. A detailed data column is shown Figure 3-6-3-1.
3-6-2 Future Policy
As shown in Table 3-6-3-1, information posted on the human resources network varies greatly between different countries and regions. This is not because some countries and regions have fewer experts than others, but because of the way the Center chose areas for survey in the initial year. We plan to gather more information from areas for which information was scarce in fiscal 1998. We will also improve the service and interface by listening to what users have to say.
Table 3-6-3-1: By-country Human Resources Information
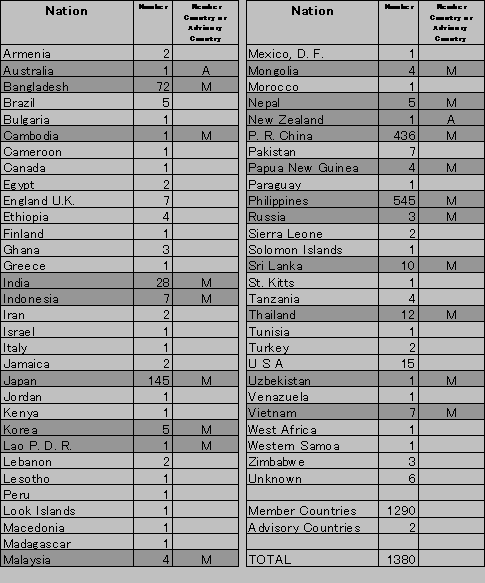
Table 3-6-3-2: Search Results by Disaster Category
| Disaster |
Number |
Disaster |
Number |
|
|
Typhoon |
1 |
Flood |
66 |
|
|
Cyclone |
17 |
Drought |
20 |
|
|
Hurricane |
0 |
Earthquake |
101 |
|
|
Tsunami |
3 |
Volcanic Eruption |
36 |
|
|
Tidal Wave |
0 |
Forest Fire |
4 |
|
|
Landslide |
1 |
|||
ü@
ü@
Fig. 3-6-3-1: Detailed Data (Sample)